AICRP on Nematodes in Cropping Systems
The varied agro-climatic conditions and soils coupled with agricultural cultivation throughout the year have increased nematode pest activities in West Bengal causing a considerable damage to many important crops. Introduction of the project “All India Coordinated Research Project on Plant Parasitic Nematodes with Integrated Approach for their control” by I.C.A.R. in Bidhan Krishi Viswavidyalaya has provided ample opportunity for experimentation of specific problems prevailing in the state and thereby formulating suitable management practices in combating those enemies to make a better harvest. The project is operating in the Directorate of Research, B.C.K.V located at Kalyani.
Year of start/establishment of the Project: 1988
Staff Strength (Scientific/Technical or Supporting) in Full Details:
One Assistant Nematologist
Infrastructure Available:
- Nematology laboratory for working of PG Students (M.Sc/Ph.D)
- Sick Plot for Root Knot and reniform nematodes at Central Research Farm in Gayeshpur, Kalyani.
- Net house and Micro plot for pilot trials for maintenance of root knot nematode populations from different states of India.
- Open field plot (in the Directorate Building) for maintenance and supply of host differentials for identification of races of major species of root knot nematode in India.
- Other facilities for testing of populations for host reactions, varietal screening and pathogenicity of root knot nematodes
Mandate/Objectives:
- To develop state-wise distribution maps of Nematodes
- To identify the areas receiving infestation of specific nematodes pest in crops
- To make bio-ecological studies of certain important nematodes
- To evaluate different varieties/lines towards their resistance against specific nematode species.
- To ascertain yield losses in economically important crops due to nematode attack.
- To evolve integrated control measures for the nematode pests.
- To determine cropping systems for nematode management.
- To demonstrate of nematode management technologies in rice vegetables and pulses.
No. of Trials Allocated/Conducted During 2013-18:
| Year | No. of trials |
|---|---|
| 2013-14 | 33 |
| 2014-15 | 33 |
| 2015-16 | 30 |
| 2016-17 | 30 |
| 2017-18 | 30 |
| 2018-19 | |
| 2019-20 |
Salient Findings:
- Application of bioagents which one helped in reduction of root galling due to M. graminicola and enhancement of average grain yield of rice to the extent of above 50%.
- Addition of organic matter in each year through crop sequences, increase the population trend of saprozoic nematodes and reverse in case of plant parasitic nematodes.
- Soil application of neem cake @ 100g/m2 + Trichoderma viride @ 2.5 kg/ha proved very effective and increased cowpea yield to the extent of 15.5%.
Recommendations at State/National Levels (Variety/ Technologies/Patenting etc):
- Management of Meloidogyne graminicola in rice by nursery bed treatment with Pseudomonas flurescens @ 20 g/m2.
- Hot water treatment at 52-54 ºC for 10-15 min to denematise the seeds infected with white tip nematode in rice.
- Overnight soaking of bulbs either in plain water or in 5% neem seed kernel extract against foliar nematode in tuberose.
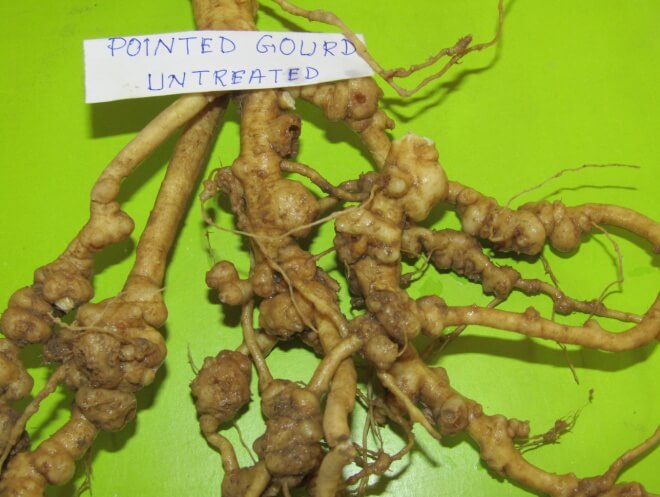
- Neem cake @ 30g/plant as spot treatment 10 days prior to planting of pointed gourd against root knot nematode.
- Soil application of neem cake @ 100g/m2 + Trichoderma viride @ 2.5 kg/ha effective against RKN in cowpea .
- Soil application of Pseudomonas fluorescens @ 20 g/ m2 and Paring + HWT (550C) + carbofuran @ 0.5g a.i./plant + neem cake @1kg/plant is effective in reduction of root-knot nematode infestation of banana cv. Grand Naine .
- Use of non host crop rotation with ground nut, black gram, mustard and potato to bringing down the population of RKN in rice.
- Growing tolerant varities like Prajwal, Phule Rajni, Shringer against foliar nematode of tuberose.
- Seed treatments with P. lilacinus @ 20 g / kg of seed + soil application of P. lilacinus at 2.5kg with FYM 2.5t/ha against RKN in okra
- Nematode parasitic fungus, Paecilomyces lilacinus @ 50g/m2 in nursery bed + P. lilacinus @5kg/ha + 2.5 ton FYM/ha in tomato.
- Soil application of P. fluorescens 20 g/ m2+ Neem cake @100 g/m²) against RKN in cowpea.
Achievements:
- Prepared a district-wise distribution map of phytonematodes infecting major crops in West Bengal
- Impact studies of rice root knot nematode in hot spot of Nadia district on the yield of rice varieties showed that the nematode was caused around 23 % yield loss under main field situation. The root knot nematode in jute (JRO-524) was found to cause crop loss to the tune of 25% in Nadia district of West Bengal.
- Preliminary screening of the 103 rice germplasms against, Meloidogyne graminicola and 124 okra, 60 chickpea, 23 fieldpea, 22 lentil, 14 mungbean, 12 urdbean and 26 pigeonpea germplasms against Meloidogyne incognita race 2 revealed that only 33 germplasm of rice, 48 of okra, 9 chickpea, 7 fieldpea, 8 lentil, 3 mungbean and 19 pigeonpea germplasms were identified as resistant.
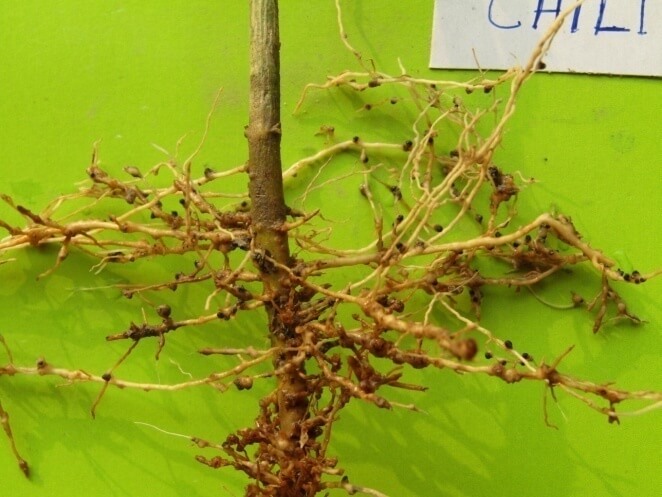
- Generated yield loss information due to root knot on cucumber (26%) jute (7%), pointed gourd (24%), brinjal (6%), tomato (8%) and chilli (11%).
- Biopesticide formulation of Paecilomyces lilacinus/Trichoderma harzianum (cfu 2x 106) as seed treatment @20g/ kg seed + P. lilacinus / T. harzianum (cfu 2x 106) @ 2.5 kg along with 2.5 tons of FYM /ha prior to sowing of okra suppressed (26 to 60%) soil nematode population and enhancing fruit to the extent of 8-15% over untreated control in okra.
- In managing of phytonematodes by crop rotation, the population of reniform nematode (R. reniformis) was significantly reduced where paddy was grown in the crop sequences.
- Soil application of Pseudomonas fluorescens @ 20 g/ m2 and Paring + HWT (550C) + carbofuran @ 0.5g a.i./plant + neem cake @1kg/plant (T2) proved very effective in reduction of root-knot nematode infestation and enhancement yield of banana cv. Grand Naine by 38%.
- Basic researches on root knot nematodes – maintained national collection of root knot nematode populations, identified species and races. Populations characterized based on morphological, biochemical and molecular approaches. Twenty-two gene sequences of rDNA (ITS-I and ITS-II) of Meloidogyne species have been submitted to NCBI-database.
- Soil solarisation with 25m m sheet for 15 days during May + carbofuran @ 1 kg a.i/ha at 45 DAT found effective against M. graminicola in producing higher yield (2.75t/ha) and reduction of nematode populations (j2) in soil (26-42.5%).
- Soil application of P. fluorescens 20 g/ m2+ Neem cake @100 g/m²) resulted in highest yield (3.17 t/ha) proved very effective in increasing cowpea yield .
- Seed treatment with P. lilacinum @ 2.5 ml/kg + Pochonia chlamydosporia @ 2.5 ml/kg followed by soil application of vermicompost @ 2.5 ton/ha enriched with P. lilacinum and Pochonia chlamydosporia (each @ 5 ml/kg) was responsible to increasing the yield of okra to 24%.